Choosing the Right Tool: Selecting the Ideal Infiltration Cannula for Surgical Procedures
Introduction
In surgical procedures, the selection of the right tools is crucial for achieving successful outcomes. Among these tools, the infiltration cannula plays a vital role in delivering fluids such as anesthetics and tumescent solutions. Choosing the ideal infiltration cannula requires a comprehensive understanding of various factors, including size, design, and material. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of these factors to assist surgeons and medical professionals in selecting the most appropriate infiltration cannula for their surgical procedures.
1. Factors to Consider When Selecting an Infiltration Cannula
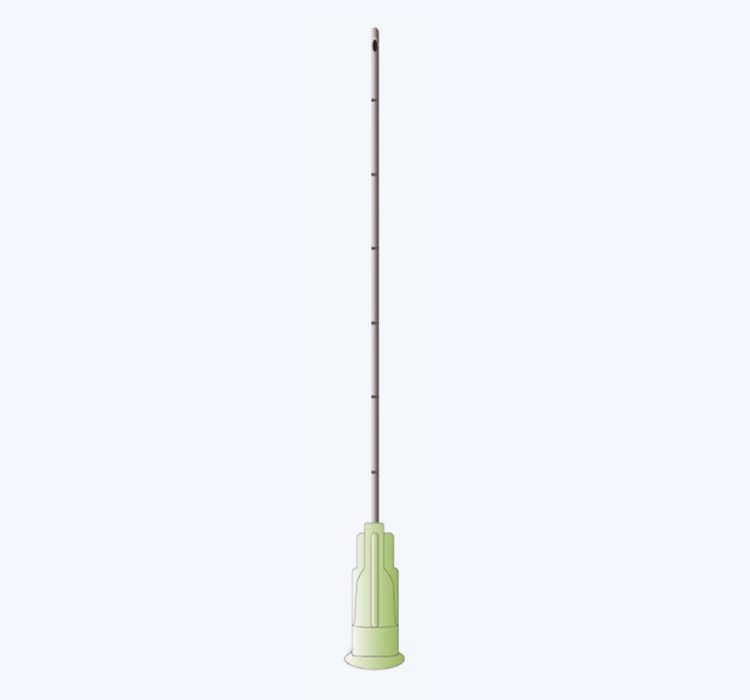
1.1 Size and Gauge
One of the primary factors to consider when choosing an infiltration cannula is its size or gauge. Cannula sizes typically range from 14 to 25 gauge, with smaller numbers indicating larger cannulas. The size of the cannula influences the flow rate of the solution being injected and the tissue trauma caused during infiltration. Smaller cannulas (larger gauge sizes) are suitable for delicate areas or procedures that require minimal tissue disruption. On the other hand, larger cannulas (smaller gauge sizes) may be preferred for rapid infiltration or procedures involving denser tissues.
1.2 Design and Tip Configuration
Another important consideration when selecting an infiltration cannula is its design and tip configuration. There are various types of cannula designs available, including blunt-tip, side-hole, multiport, and fenestrated cannulas. Blunt-tip cannulas are commonly used for lymphosuction and fat grafting procedures due to their reduced risk of tissue damage. Side-hole cannulas are designed to disperse the infiltrating solution evenly, making them suitable for larger areas. Multiport and fenestrated cannulas provide enhanced control and precision, allowing surgeons to target specific areas or perform intricate procedures.
2. Material Selection for Infiltration Cannulas
The choice of material used in the construction of an infiltration cannula is crucial for its performance and durability. Common materials include stainless steel, plastic, and disposable polymers.
2.1 Stainless Steel
Stainless steel infiltration cannulas are widely used due to their excellent strength and durability. They are resistant to bending or kinking, ensuring reliable performance throughout surgical procedures. Stainless steel cannulas can be reused after proper sterilization, making them a cost-effective option for hospitals and clinics. However, care must be taken to prevent corrosion and to ensure thorough cleaning and sterilization between uses.
2.2 Plastic Cannulas
Plastic infiltration cannulas offer several advantages, such as being disposable, reducing the risk of contamination, and eliminating the need for reprocessing and sterilization. Plastic cannulas are typically made from materials like polyethylene or polypropylene and are available in various sizes and configurations. These cannulas are lightweight, flexible, and can be easily manipulated during procedures, improving overall ergonomics. However, plastic cannulas may be prone to bending or breaking, requiring careful handling.
3. Special Considerations for Specific Surgical Procedures
3.1 Tumescent Liposuction
Tumescent liposuction is a popular cosmetic procedure that involves injecting large volumes of tumescent solution into the subcutaneous fat layer before performing liposuction. For this procedure, the ideal infiltration cannula should have a large gauge size to allow rapid and efficient infiltration of the tumescent solution. Side-hole cannulas or multiport cannulas provide even distribution and help prevent overfilling in specific areas, minimizing the risks associated with the procedure.
3.2 Fat Grafting
In fat grafting procedures, where adipose tissue is harvested from one area of the body and transferred to another, blunt-tip cannulas are commonly used. These cannulas have a rounded or olive-shaped tip that reduces the risk of damaging the delicate harvested fat cells, ensuring better graft survival rates. Additionally, cannulas with smaller gauges are preferred to minimize trauma during both harvesting and injection phases.
3.3 Subdermal Implant Placement
When placing subdermal implants, such as chin or cheek implants, precision and control are crucial. Therefore, the use of fenestrated cannulas is recommended. The fenestrations on the cannula's side walls allow for targeted infiltration of the implant pocket, avoiding damage to surrounding tissues. Smaller gauge sizes are often preferred in these procedures to minimize trauma and scarring.
4. Conclusion
Choosing the right infiltration cannula is an essential step in ensuring successful surgical outcomes. Surgeons and medical professionals must carefully consider various factors, including size, design, and material, to select the ideal cannula for each specific procedure. Proper understanding of these factors and their implications will aid in reducing tissue trauma, improving patient comfort, and achieving optimal results. By making informed decisions, healthcare providers can enhance their surgical techniques, ultimately benefiting their patients' overall experience and recovery.

 Español
Español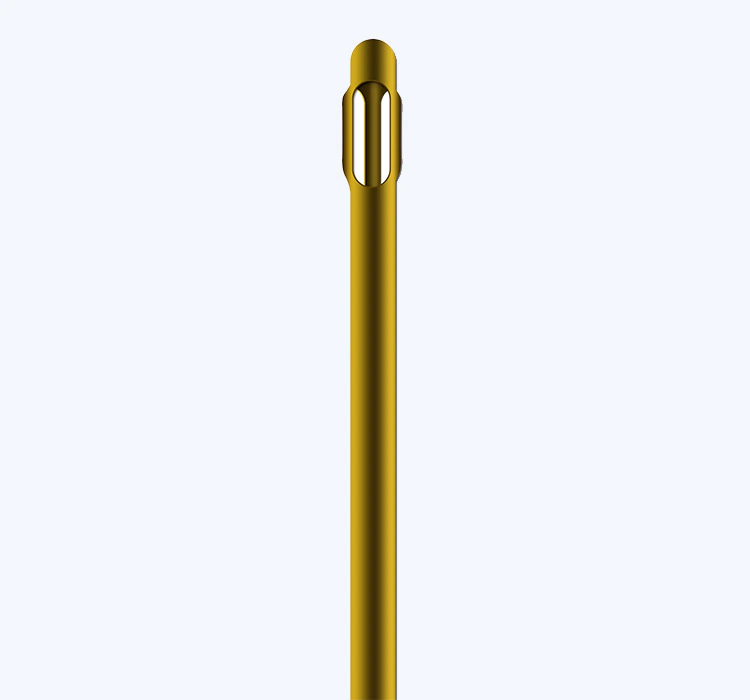



 Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou
Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou Email :
Email :  WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
