Infiltration Cannulas in Maxillofacial Surgery: Pain-Free Procedures
Infiltration Cannulas in Maxillofacial Surgery: Pain-Free Procedures
Introduction
Maxillofacial surgery is a specialized field of medicine that deals with various conditions and injuries involving the mouth, jaw, face, and neck. While surgical procedures in this area often produce positive outcomes, they can also result in significant postoperative pain and discomfort for the patients. Infiltration cannulas have emerged as a valuable tool in maxillofacial surgery, offering pain alleviation and improved patient experience during and after procedures. This article explores the significance of infiltration cannulas in maxillofacial surgery and highlights their benefits in pain management.
The Role of Infiltration Cannulas in Maxillofacial Surgery
Infiltration cannulas are thin, hollow tubes made of medical-grade materials, designed to deliver local anesthesia and other medications directly to the surgical site. These cannulas facilitate the controlled release of fluids, allowing precise infiltration of anesthetic agents into target tissues. In maxillofacial surgery, infiltration cannulas help in achieving effective pain relief by directly injecting local anesthetics into the affected area, numbing the region and reducing operative discomfort.
Advantages of Using Infiltration Cannulas in Maxillofacial Procedures
1. Enhanced Patient Comfort: Infiltration cannulas significantly improve patient comfort during maxillofacial procedures by providing targeted pain relief. By directly administering local anesthetics to the surgical site, infiltration cannulas greatly reduce the need for systemic anesthesia, leading to fewer side effects and a quicker recovery for the patient.
2. Reduced Bleeding: Infiltration cannulas can also play a role in minimizing bleeding during maxillofacial surgery. By delivering medications directly to the site of operation, these cannulas constrict blood vessels, reducing the risk of excessive bleeding. This advantage not only provides better visibility for the surgeon but also contributes to a smoother surgical process.
3. Optimal Medication Delivery: Infiltration cannulas allow surgeons to deliver local anesthetics precisely to the targeted tissues. This controlled delivery ensures that an adequate amount of medication reaches the nerve endings, providing effective pain relief. Furthermore, infiltration cannulas can be used to administer other drugs such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications, aiding in postoperative recovery.
4. Faster Recovery: Since infiltration cannulas reduce the need for general anesthesia and minimize surgical trauma, patients experience a faster recovery period. The targeted pain relief provided by these cannulas allows patients to resume normal oral functions sooner, improving their overall quality of life post-surgery.
Different Types of Infiltration Cannulas
1. Bevel-Ended Cannulas: These cannulas have a pointed, beveled tip that helps in precise insertion and infiltration. Bevel-ended cannulas are commonly used in maxillofacial surgery when accurate drug placement is critical.
2. Tapered Cannulas: Tapered cannulas feature a narrow, tapered design, allowing for easier penetration into tissues with minimal trauma. These cannulas are often used for delicate procedures where precise placement of anesthesia is vital.
3. Blunt Cannulas: Blunt cannulas have a rounded tip, reducing the risk of accidental punctures and injury to surrounding structures. These cannulas are particularly useful when administering medication near sensitive areas such as nerves or blood vessels.
4. Multiport Cannulas: Multiport cannulas have multiple openings along the shaft, allowing for the distribution of anesthesia or other drugs to a larger area. These cannulas are suitable for surgeries that require a broader coverage of analgesic agents.
5. Flexible Cannulas: Flexible cannulas are made of pliable materials that can bend and adapt to different tissue contours. These cannulas offer greater maneuverability, making them ideal for surgeries that involve complex anatomical structures.
Procedure Guidelines for the Use of Infiltration Cannulas
1. Proper Patient Assessment: Before utilizing infiltration cannulas, a comprehensive patient assessment must be conducted, including a review of medical history, allergies, and any ongoing medications. This assessment ensures the safe and effective use of infiltrative anesthesia.
2. Aseptic Technique: Infiltration cannulas should be inserted using strict aseptic technique to prevent the risk of infection. Proper hand hygiene, sterilization of equipment, and the use of sterile drapes and gloves are essential to maintain a clean surgical environment.
3. Accurate Placement: Surgeons must ensure accurate placement of infiltration cannulas to deliver the anesthetic or medication precisely. This may involve the use of imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, to identify the target area and guide cannula insertion.
4. Monitoring and Safety: Continuous monitoring of vital signs and the patient's response to anesthesia is crucial during maxillofacial surgery. Careful observation of any adverse reactions or complications related to anesthesia allows prompt intervention and improved patient safety.
5. Postoperative Care: After the surgical procedure, proper postoperative care is essential to ensure patient comfort and optimal recovery. Adequate pain management, follow-up appointments, and clear instructions on oral hygiene are important factors that contribute to successful outcomes.
Conclusion
Infiltration cannulas have revolutionized the field of maxillofacial surgery by providing pain relief and improved patient experiences during and after procedures. These thin, hollow tubes allow targeted delivery of local anesthesia and other medications, resulting in enhanced patient comfort, reduced bleeding, and faster recovery. The various types of infiltration cannulas offer flexibility and precision for different surgical scenarios. Nevertheless, adherence to proper procedures and careful patient assessment remain crucial to ensure the safe and effective use of infiltration cannulas in maxillofacial surgery.

 Español
Español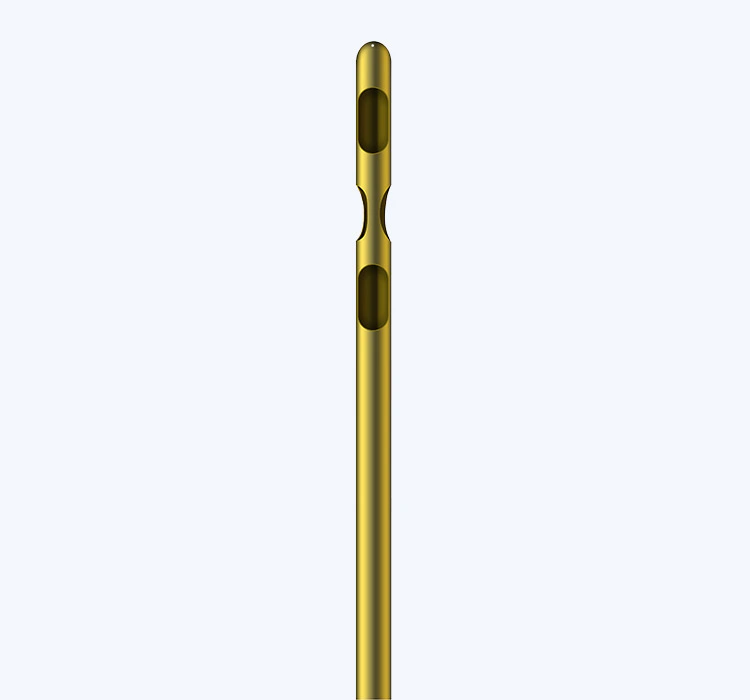



 Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou
Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou Email :
Email :  WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
