Microaire Cannulas vs. Traditional Techniques: A Comparative Analysis
Introduction
Microaire cannulas have emerged as a revolutionary technique for various surgical procedures, offering numerous advantages over traditional techniques. This comparative analysis aims to delve into the differences between microaire cannulas and traditional techniques, exploring their respective benefits, limitations, and outcomes. By understanding the nuances and potential benefits of using microaire cannulas, surgeons can make informed decisions that may optimize patient outcomes and improve surgical procedures.
The Evolution of Microaire Cannulas: A Brief Overview
Microaire cannulas represent a significant advancement in surgical instruments, providing enhanced precision and control during procedures. Unlike traditional techniques that rely on manual force, microaire cannulas utilize a pneumatic design that enables surgeons to execute delicate movements and maneuvers with greater accuracy. This technology has proven particularly useful for plastic surgeons, as it allows for precise fat extraction and reshaping while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
Microaire cannulas feature an intricate design that includes a hollow tube connected to a pneumatic power source. The cannula's distal end incorporates a small aperture that generates pulsating vibrations when high-frequency air is released from the generator. These vibrations facilitate the breakup of fat tissue, making it easier to aspirate and creating a sculpted aesthetic outcome.
The Advantages of Microaire Cannulas
Microaire cannulas offer several advantages over traditional techniques, making them an attractive option for surgeons in various specialties. Here, we explore some of their key benefits:
Precision and Flexibility
By utilizing pneumatic power, microaire cannulas enable surgeons to perform precise movements and achieve a high level of control during procedures. The pulsating vibrations generated by the cannula's distal aperture allow for smoother and more uniform tissue disruption, ensuring a more symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing outcome. Additionally, the flexibility of microaire cannulas allows surgeons to navigate intricate anatomical structures more easily, leading to reduced collateral tissue damage and a faster recovery for patients.
Enhanced Fat Removal
One of the primary uses of microaire cannulas is for liposuction procedures. In comparison to traditional manual techniques, microaire cannulas are better at removing larger volumes of fat in a shorter amount of time. The vibrating action of microaire cannulas results in more efficient fat emulsification and extraction, reducing the physical strain on the surgeon and minimizing patient discomfort during the procedure. This increased effectiveness can also lead to shorter operative times, enabling surgeons to perform multiple procedures in a single session.
Reduced Surgeon Fatigue
Traditional surgical techniques often rely on repetitive manual movements, which can lead to surgeon fatigue and decreased precision over time. Microaire cannulas mitigate this issue by utilizing pneumatic power to perform the majority of the work. The reduced physical effort required by the surgeon allows for more controlled and accurate movements throughout the procedure. Consequently, surgeons can maintain optimal performance for longer durations, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Minimized Postoperative Bruising and Swelling
Postoperative bruising and swelling are common concerns following surgical procedures, particularly in aesthetic surgeries. Microaire cannulas, due to their precise and gentle vibrating motion, result in less trauma to the surrounding tissues. This minimized trauma often translates to reduced bruising and swelling, leading to more comfortable and cosmetically favorable recoveries for patients.
Improved Patient Safety
Microaire cannulas have integrated safety features that contribute to a decreased risk of complications during surgical procedures. Some models include a pressure-sensitive system that automatically stops the cannula's vibration if it encounters resistance. This prevents excessive tissue damage or unintended perforations, ensuring patient safety and minimizing the need for subsequent corrective procedures.
The Limitations of Microaire Cannulas
While microaire cannulas offer numerous advantages, it is important to acknowledge their limitations to make informed decisions when choosing surgical techniques. Below, we discuss some of the limitations associated with the use of microaire cannulas:
Cost
Microaire cannulas generally require a larger initial investment compared to traditional surgical instruments. The advanced technology and precision engineering of microaire cannulas contribute to their higher price point. However, considering the benefits they offer, many surgeons believe that the long-term advantages and improved patient outcomes outweigh the initial costs associated with acquiring these devices.
Learning Curve
Given their unique design and capabilities, surgeons may require additional training and practice to become proficient in using microaire cannulas effectively. Familiarizing oneself with the nuances of the equipment, such as understanding optimal power settings and proper technique, is crucial for achieving desirable outcomes. Therefore, surgeons considering the adoption of microaire cannulas should invest time in gaining hands-on experience and possibly attending specialized training workshops.
Restricted Applications
While microaire cannulas excel in certain surgical procedures, they may not be the ideal choice for every case. The vibrating action of microaire cannulas may not be suitable for delicate or highly vascular areas, where the potential for tissue trauma or vascular damage is significant. In such instances, surgeons may opt for traditional techniques that provide greater tactile feedback and offer more control over the procedure.
Summary
Microaire cannulas have revolutionized various surgical procedures by offering enhanced precision, reduced trauma, and improved outcomes. Their pneumatic design, coupled with pulsating vibrations, enables surgeons to perform delicate maneuvers with greater control and flexibility. By utilizing microaire cannulas, surgeons can achieve better fat removal results, reduce surgeon fatigue, minimize postoperative bruising and swelling, and enhance patient safety.
However, surgeons must also consider the limitations of microaire cannulas, such as the higher initial costs and the learning curve associated with their use. Additionally, the restricted applicability of microaire cannulas in certain anatomical areas may necessitate the continued use of traditional techniques in some surgical cases.
Overall, this comparative analysis highlights the potential advantages of microaire cannulas in various surgical applications while acknowledging their limitations. By keeping abreast of advancements in surgical instrumentation, surgeons can make informed decisions that optimize patient outcomes and contribute to ongoing advancements in the field of surgery.

 Español
Español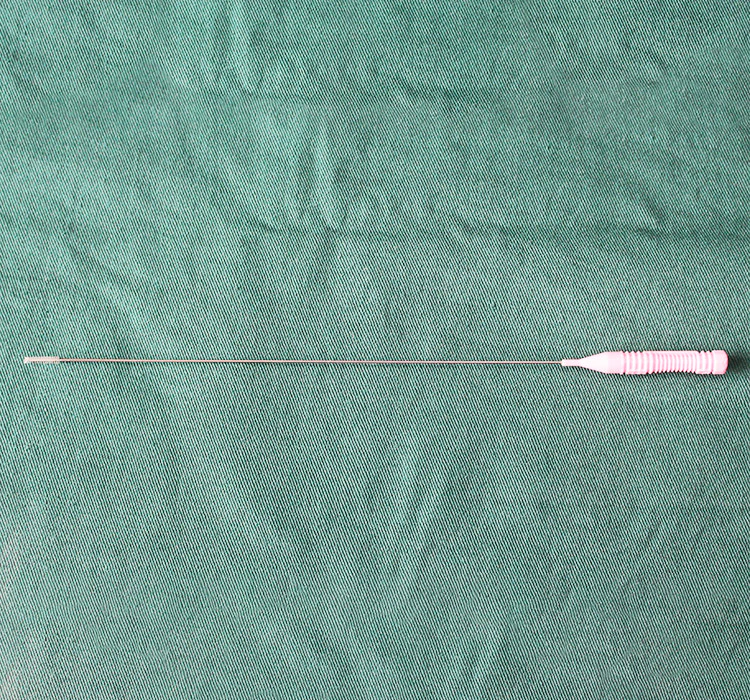



 Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou
Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou Email :
Email :  WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
