Preventing Complications with Infiltration Cannulas: Best Practices for Healthcare Providers
Infiltration cannulas are an essential tool used by healthcare providers for various medical procedures. However, if not used properly, they can lead to unwanted complications such as tissue damage, infection, and nerve injury. In this article, we will discuss the best practices for healthcare providers to prevent complications when using infiltration cannulas.
Understanding Infiltration Cannulas
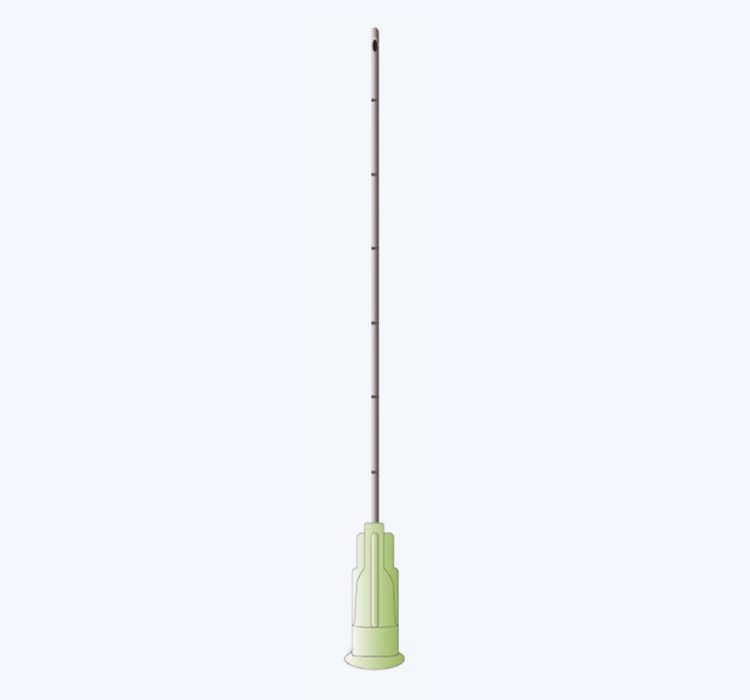
Infiltration cannulas are thin, hollow tubes used to deliver fluids, medications, or local anesthetics into the body's tissues. They are commonly used in procedures such as liposuction, wound irrigation, and epidural injections. These cannulas come in different lengths, gauges, and designs, depending on the specific procedure and patient requirements.
When selecting an infiltration cannula, healthcare providers should consider factors such as the intended use, patient's anatomy, and the viscosity of the solution to be delivered. Using the correct size and type of cannula is crucial to ensure precise delivery and minimize the risk of complications.
Proper Technique and Positioning
One of the most critical aspects of using infiltration cannulas is proper technique and positioning. Healthcare providers should always follow established protocols and guidelines when performing procedures involving infiltration cannulas. This includes proper sterilization of the equipment, maintaining aseptic technique, and ensuring proper placement of the cannula in the target tissue.
When inserting the cannula, healthcare providers should use a slow, controlled motion to avoid sudden movements that may cause tissue damage or injury. The cannula should be inserted at the correct angle and depth to reach the desired tissue while minimizing the risk of complications. Careful attention should be paid to the entry site to prevent leakage or misplacement of the cannula.
Monitoring and Assessment
Monitoring the patient during and after the infiltration procedure is essential to detect any signs of complications early. Healthcare providers should closely observe the patient for signs of infection, bleeding, swelling, or pain at the cannula insertion site. Any abnormalities should be promptly reported and addressed to prevent further complications.
In addition to monitoring the patient, healthcare providers should also assess the effectiveness of the infiltration procedure. This may include evaluating the distribution of the delivered solution, assessing the patient's response to the treatment, and ensuring that the desired outcomes are achieved. Adjustments to the technique or equipment may be necessary based on the assessment results to optimize patient outcomes.
Complication Management and Reporting
Despite best efforts to prevent complications, healthcare providers should be prepared to manage any adverse events that may occur during or after the infiltration procedure. This may include treating infections, controlling bleeding, managing pain, or addressing tissue damage caused by the cannula.
It is essential for healthcare providers to have protocols in place for managing complications and reporting any adverse events to the appropriate authorities. This ensures that incidents are properly documented, investigated, and addressed to prevent similar occurrences in the future. Healthcare providers should also educate patients on the potential risks and benefits of infiltration procedures to empower them to make informed decisions about their care.
Training and Continuing Education
Lastly, healthcare providers should continually seek training and education to stay updated on the latest techniques, technologies, and guidelines related to infiltration cannulas. This may include attending workshops, conferences, or courses on cannula use, as well as participating in hands-on training sessions to practice proper techniques.
Continuing education helps healthcare providers stay current with best practices, emerging trends, and research findings in the field of infiltration cannulas. By investing in ongoing training and professional development, healthcare providers can enhance their skills, improve patient outcomes, and reduce the risk of complications associated with infiltration procedures.
In conclusion, using infiltration cannulas carries inherent risks, but by following best practices and guidelines, healthcare providers can minimize the likelihood of complications and ensure safe and effective patient care. From understanding the different types of cannulas to implementing proper technique, monitoring patients, managing complications, and pursuing ongoing education, healthcare providers play a crucial role in preventing adverse events associated with infiltration procedures. By prioritizing patient safety and quality care, healthcare providers can uphold the highest standards of practice and deliver optimal outcomes for their patients.

 Español
Español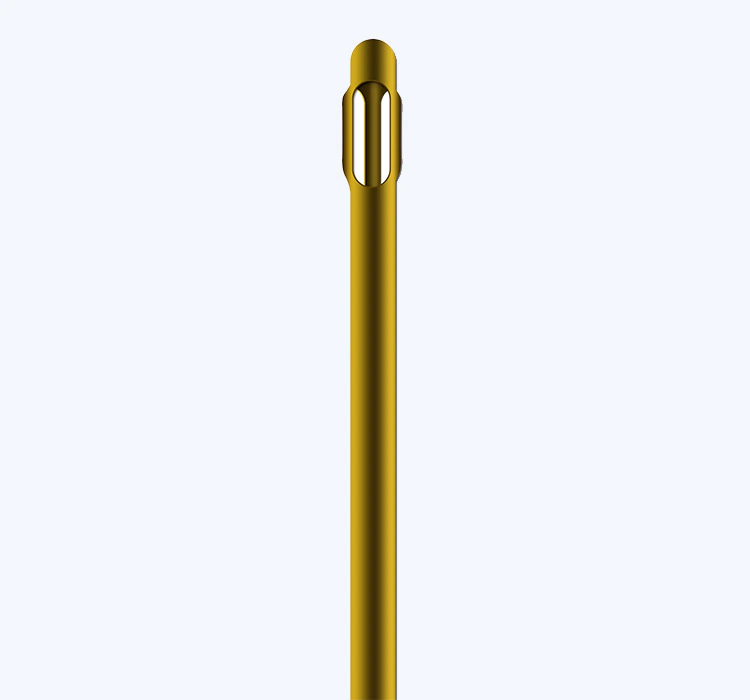



 Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou
Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou Email :
Email :  WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
