The Science of Fat Grafting: Understanding Fat Harvesting Cannula Techniques
Article
1. Introduction to Fat Grafting and its Importance in Aesthetic Procedures
2. An In-depth Look at Fat Harvesting Techniques and Different Cannula Options
3. The Science Behind Fat Grafting: Understanding the Physiology of Adipose Tissue
4. Factors Affecting Fat Survival and Overall Grafting Success
5. Practical Considerations and Precautions to Optimize Fat Grafting Outcomes
Introduction to Fat Grafting and its Importance in Aesthetic Procedures
Fat grafting, also known as fat transfer or lipofilling, is a popular technique that has revolutionized various cosmetic and reconstructive procedures. This procedure involves the removal and redistribution of a patient's own fat cells to enhance or restore volume in different areas of the body. Fat grafting offers a natural-looking and long-lasting solution for those seeking enhancement in areas such as the face, breasts, buttocks, and hands.
An In-depth Look at Fat Harvesting Techniques and Different Cannula Options
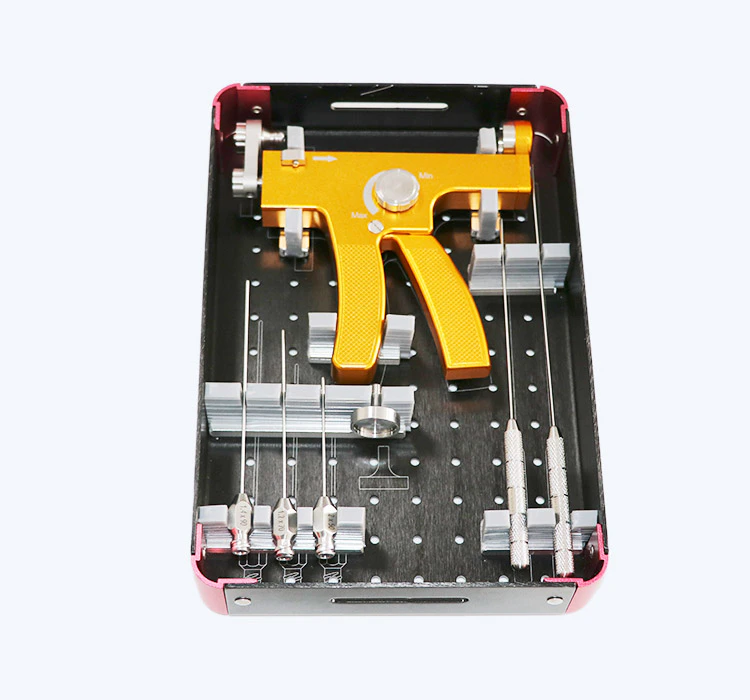
The success of fat grafting largely depends on the technique used for fat harvesting. The procedure involves the removal of excess fat cells from one part of the body, typically through liposuction, and then carefully injecting them into the desired area. To achieve optimal outcomes, surgeons must have a thorough understanding of different fat harvesting techniques and the type of cannula (a hollow tube used in liposuction to aspirate fat) to use in each case.
Several cannula options are available for fat harvesting, including traditional liposuction cannulas, power-assisted liposuction cannulas, and novel technologies such as the vibration-assisted liposuction cannulas. Each cannula type offers unique advantages and considerations based on factors such as the target area, fat characteristics, and the surgeon's preference.
The Science Behind Fat Grafting: Understanding the Physiology of Adipose Tissue
Fat grafting works on the principle of utilizing the body's adipose tissue, commonly known as fat. Adipose tissue is made up of adipocytes, which are specialized cells responsible for storing triglycerides. These cells perform essential metabolic functions and play a crucial role in maintaining energy balance and supporting overall health.
The success of fat grafting relies on the survival and integration of the transplanted adipocytes. Once fat cells have been harvested from a donor site, they must be carefully processed and injected into the recipient area. While the mechanism behind their integration is not fully understood, it is widely believed that transplanted fat cells establish a new blood supply and develop a network of vascular connections to survive long-term.
Factors Affecting Fat Survival and Overall Grafting Success
While fat grafting can provide impressive results, it is important to consider several factors that can influence fat survival and overall grafting success. These factors include the technique used for harvesting and processing fat cells, the quality of the harvested adipose tissue, the injection technique, and the recipient site characteristics.
Furthermore, patient-related factors such as age, smoking, and coexisting medical conditions can also affect fat grafting outcomes. Research suggests that younger patients tend to have higher fat survival rates compared to older individuals due to differences in angiogenic potential, tissue quality, and overall regenerative capacity. Therefore, it is crucial to assess each patient individually and address any potential limitations before proceeding with fat grafting.
Practical Considerations and Precautions to Optimize Fat Grafting Outcomes
To achieve optimal fat grafting outcomes, surgeons should consider various practical factors and take necessary precautions. Firstly, careful preoperative planning is essential to determine suitable donor sites and recipient areas, ensuring the patient's goals align with achievable outcomes. Moreover, meticulous attention should be given to harvesting techniques to avoid trauma to the adipose tissue, which can lead to reduced fat cell viability.
Additionally, surgeons must optimize the processing of harvested fat cells to remove any contaminants, blood, or anesthetic solutions before injection. This step ensures the survival and integration of transplanted adipocytes within the recipient site. Lastly, surgeons must employ proper injection techniques that involve depositing small aliquots of fat at multiple depths to facilitate revascularization and optimize fat cell survival.
Conclusion
Fat grafting has become an indispensable tool in various aesthetic procedures, offering patients a safe and effective means to enhance their appearance or address volume loss. Understanding the science behind fat grafting, selecting appropriate cannulas, and adopting meticulous techniques are essential for achieving successful outcomes. By considering various factors that influence fat survival and implementing practical precautions, surgeons can optimize fat grafting results and provide their patients with natural, long-lasting improvements.

 Español
Español



 Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou
Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou Email :
Email :  WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
