The Science of Micro Fat Grafting: How Cannula Design Impacts Fat Survival
Introduction:
Micro fat grafting is an innovative technique used in cosmetic and reconstructive surgeries to transfer small amounts of fat from one part of the body to another. This procedure has gained popularity in recent years due to its natural-looking results and minimal invasiveness. However, the success of micro fat grafting greatly depends on the design of the cannula used during the procedure. In this article, we will explore the science behind micro fat grafting and how different cannula designs can impact fat survival.
The Basics of Micro Fat Grafting
Micro fat grafting, also known as micro lipoinjection or micro fat transfer, involves harvesting small amounts of fat through liposuction from areas of excess, such as the abdomen or thighs, and re-implanting it into areas of volume loss, like the face or hands. The harvested fat is processed to remove impurities and excess fluids, leaving only viable fat cells for injection. This technique is ideal for adding volume, filling in wrinkles and lines, and improving overall skin quality.
The key to successful micro fat grafting lies in the survival of the transplanted fat cells. When fat is transferred from one area to another, it relies on the formation of new blood vessels to receive nutrients and oxygen for survival. If the fat cells do not establish a blood supply quickly, they can die off, leading to poor outcomes. This is where the design of the cannula plays a crucial role.
The Impact of Cannula Design on Fat Survival
Cannulas are thin, hollow tubes used to remove and inject fat during micro fat grafting procedures. The design of the cannula can affect the efficiency of fat harvesting, processing, and injection, ultimately influencing fat survival rates. There are several key factors to consider when evaluating cannula design:
Cannula Diameter and Length
The diameter and length of the cannula can significantly impact the fat survival rate. A larger cannula diameter may cause more trauma to the fat cells during harvesting, leading to decreased viability. On the other hand, a longer cannula may not provide enough control during injection, resulting in uneven fat distribution. Finding the right balance between diameter and length is essential for optimal fat survival.
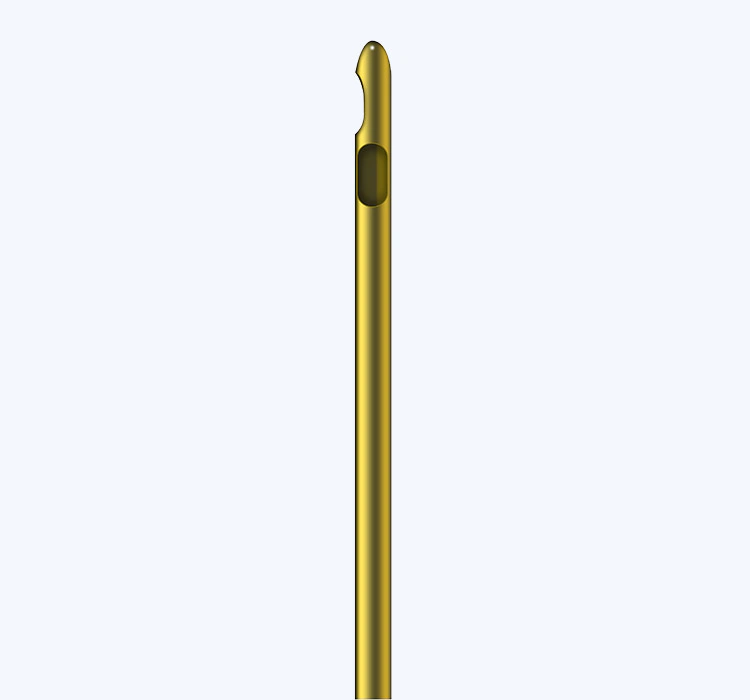
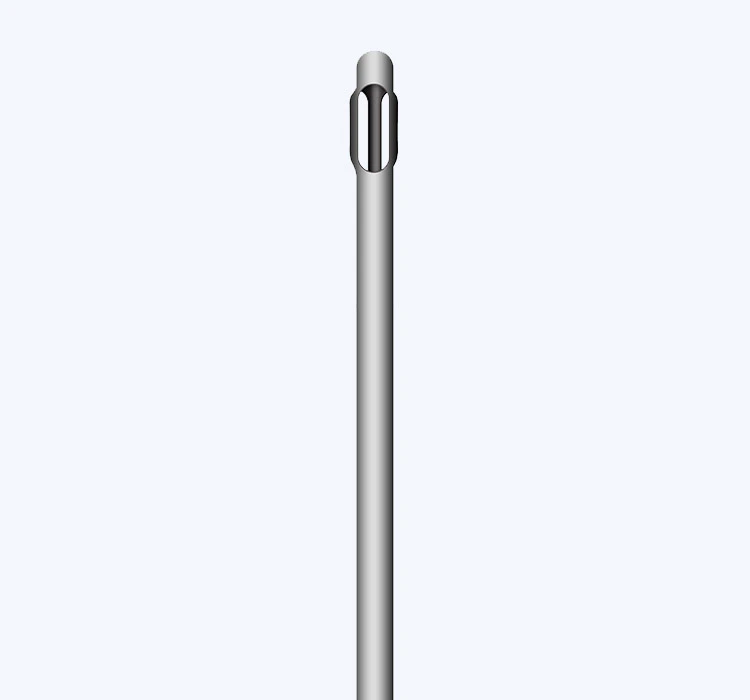
Cannula Tip Design
The tip of the cannula plays a critical role in the precision and control of fat injection. Different tip designs, such as round, blunt, or sharp tips, can influence the ease of fat deposition and the risk of damage to surrounding tissues. A rounded tip is generally preferred for smoother, more controlled injections, minimizing the risk of puncturing blood vessels or nerves.
Cannula Flexibility and Rigidity
The flexibility and rigidity of the cannula can affect the ease of maneuverability and tissue penetration during fat grafting. A too rigid cannula may cause excessive trauma to surrounding tissues, while a too flexible cannula may lack the necessary push to penetrate deeper layers. Finding a balance between flexibility and rigidity is crucial for optimal fat survival and aesthetic outcomes.
Cannula Lumen Design
The lumen of the cannula refers to the inner diameter that allows the passage of fat cells. A wider lumen can accommodate larger clusters of fat cells, improving the efficiency of fat harvesting and injection. However, a wider lumen may also increase the risk of fat cell damage during processing. Balancing the lumen design to optimize fat cell viability is essential for successful micro fat grafting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the science of micro fat grafting is a complex but rewarding field that offers natural and long-lasting results for patients seeking facial rejuvenation or volume restoration. The design of the cannula used during the procedure plays a crucial role in the success of fat survival and overall aesthetic outcomes. By understanding the impact of cannula design on fat cell viability, surgeons can tailor their technique to maximize results and minimize complications. Continuous advancements in cannula technology and techniques will further improve the efficacy and safety of micro fat grafting, ensuring optimal patient satisfaction and outcomes.

 Español
Español



 Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou
Sales Manager : Kelly Zhou Email :
Email :  WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
WhatsApp : +86 18067965386
